Choosing the right birth control method can feel overwhelming, especially when trying to avoid unwanted side effects. With so many options available, from hormonal to non-hormonal methods, it’s important to find one that suits your body, lifestyle, and health needs.
Recommended: How to Discuss Family Planning with Your Partner
In this blog, we’ll explore different birth control options, factors to consider, and how to minimize side effects. Whether you’re looking for a long-term solution or a temporary method, this guide will help you make an informed decision for your reproductive health.
Understanding Birth Control and Its Importance
Birth control plays a crucial role in reproductive health by allowing individuals to prevent pregnancy safely and effectively. It gives people the freedom to plan their families, focus on their careers, and take control of their bodies.
There are many birth control methods available, ranging from hormonal pills and injections to non-hormonal options like condoms and copper IUDs. Some methods also offer additional benefits, such as regulating menstrual cycles, reducing acne, or managing hormonal imbalances.
Recommended: Best Fertility Tracker to Avoid Pregnancy
Choosing the right birth control is important because different methods work differently for each person. Understanding your options can help you find a method that is safe, effective, and free from unwanted side effects. By learning more about birth control, you can make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Birth Control Method
Choosing the right birth control method is a personal decision that should take several factors into account to ensure effectiveness while minimizing side effects. Here are some key aspects to consider:
1. Health and Medical History
Your overall health plays a significant role in determining the best birth control method for you. If you have conditions such as high blood pressure, migraines, or a history of blood clots, certain hormonal contraceptives may not be suitable. In such cases, non-hormonal methods might be a safer alternative.
Recommended: Can Contraceptive Implant Cause Infertility?
2. Effectiveness
Different birth control methods have varying levels of effectiveness. Long-term options like implants and intrauterine devices (IUDs) offer over 99% protection, while barrier methods such as condoms and diaphragms are less effective but provide additional benefits, such as protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs). It is important to assess how crucial pregnancy prevention is when making your choice.
3. Hormonal vs. Non-Hormonal Options
Hormonal birth control, such as pills, injections, and patches, helps regulate hormones but may lead to side effects like mood swings and weight gain. Non-hormonal methods, including the copper IUD, condoms, and fertility tracking, avoid these side effects but may require more effort or discipline to use effectively.
4. Convenience and Ease of Use
Some birth control options require daily, weekly, or monthly attention, such as birth control pills or patches, while others, like IUDs or implants, provide long-term protection with little to no maintenance. If you prefer a method that does not require daily reminders, long-acting contraceptives might be the best fit.
5. Reversibility and Future Pregnancy Plans
Your reproductive goals should also influence your decision. If you plan to have children in the near future, a short-term method like birth control pills or condoms may be ideal. On the other hand, permanent solutions like tubal ligation or vasectomy are better suited for individuals who do not wish to conceive in the future.
Recommended: Can Birth Control Cause Extreme Fatigue?
6. Side Effects and Allergies
Every birth control method comes with potential side effects. Hormonal contraceptives can sometimes cause nausea, headaches, or mood swings, while barrier methods might trigger allergic reactions, especially for those sensitive to latex. Understanding your body’s tolerance will help in selecting a method that minimizes discomfort.
7. Protection Against STIs
If STI prevention is a priority, barrier methods such as male and female condoms should be considered. These are the only birth control methods that provide protection against sexually transmitted infections, making them a necessary option for individuals who are sexually active with multiple partners or those who do not have a monogamous relationship.
8. Cost and Accessibility
The financial aspect of birth control is also important. Some options, like condoms, are affordable and easily accessible, while others, such as IUDs and implants, have a higher upfront cost but last for several years, making them cost-effective in the long run. It is important to consider both short-term and long-term affordability.
9. Lifestyle and Personal Preferences
Your daily routine and comfort level with different birth control methods should also guide your decision. If you travel frequently, remembering to take a daily pill may be challenging. Similarly, if you have a fear of needles, an injectable contraceptive may not be the best option. Choosing a method that fits seamlessly into your lifestyle ensures consistency and effectiveness.
10. Consultation with a Healthcare Provider
Before making a final decision, it is always advisable to seek guidance from a doctor or healthcare professional. They can assess your medical history, lifestyle, and personal preferences to recommend the safest and most effective birth control method for you.
Recommended: Best Multivitamins For Going Off Birth Control
Birth Control Methods With Minimal Side Effects
Finding a birth control method that effectively prevents pregnancy while minimizing side effects is essential for many individuals. While all contraceptives have potential effects, some options are known for being gentler on the body. Here are some birth control methods with minimal side effects:
1. Non-Hormonal Birth Control Methods
These methods do not interfere with hormones, making them a great choice for individuals sensitive to hormonal changes.

- Copper IUD (Paragard) – A long-term, hormone-free option that can last up to 10 years. Some women experience heavier periods initially, but it does not cause hormonal side effects.
- Barrier Methods (Condoms, Diaphragms, Cervical Caps) – These prevent pregnancy without affecting the body’s natural hormonal balance. They also protect against sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
- Fertility Awareness Methods (FAMs) – Tracking ovulation through body temperature, cervical mucus, or menstrual cycles can help prevent pregnancy naturally, but it requires careful monitoring.
2. Low-Hormone Birth Control Options
For those who prefer hormonal birth control but want to reduce side effects, these methods contain lower hormone levels.
- Hormonal IUDs (Mirena, Kyleena, Skyla, Liletta) – These release a small amount of progestin and are less likely to cause mood swings or weight gain compared to birth control pills.
- Mini-Pill (Progestin-Only Pill) – Unlike combination pills, the mini-pill contains only progestin, which reduces the risk of estrogen-related side effects like nausea or headaches.
- Birth Control Patch or Vaginal Ring – These methods release a steady, low dose of hormones, reducing hormonal fluctuations that can cause side effects.
3. Permanent Birth Control Methods
For individuals who do not want children in the future, permanent options eliminate the need for daily or monthly contraception.
- Tubal Ligation (for Women) – A surgical procedure that blocks the fallopian tubes to prevent pregnancy permanently, without affecting hormones.
- Vasectomy (for Men) – A permanent and highly effective birth control option that does not alter libido or hormone levels.
Recommended: Can I Take Birth Control After Wisdom Teeth Removal?
4. Natural and Lifestyle-Based Methods
Some individuals prefer natural methods that work with their body’s cycles.
- Withdrawal Method (“Pulling Out”) – This requires careful timing and control but is not always reliable.
- Abstinence or Delayed Intercourse – The only 100% effective method of preventing pregnancy and STIs.
Natural Birth Control Methods
Natural birth control methods, also known as fertility awareness methods (FAMs), allow individuals to prevent pregnancy without the use of hormonal or barrier contraceptives. These methods rely on tracking fertility signals and making lifestyle adjustments to avoid conception. While they can be effective when used correctly, they require dedication, accuracy, and consistency. Below are some natural birth control options:
1. Calendar Method
This method involves tracking menstrual cycles over several months to predict fertile and non-fertile days. Women with regular cycles can estimate ovulation and avoid unprotected sex during their fertile window. However, irregular cycles can make this method less reliable.
2. Basal Body Temperature (BBT) Method
By measuring body temperature every morning before getting out of bed, individuals can detect slight increases that indicate ovulation has occurred. Abstaining from sex or using alternative protection during the fertile window can prevent pregnancy.
3. Cervical Mucus Method
Changes in cervical mucus consistency signal fertility. Before ovulation, mucus becomes clear, slippery, and stretchy, resembling egg whites. Avoiding unprotected sex during this time reduces the risk of pregnancy.
Recommended: Can You be on Birth Control and Donate Eggs?
4. Withdrawal Method (Pull-Out Method)
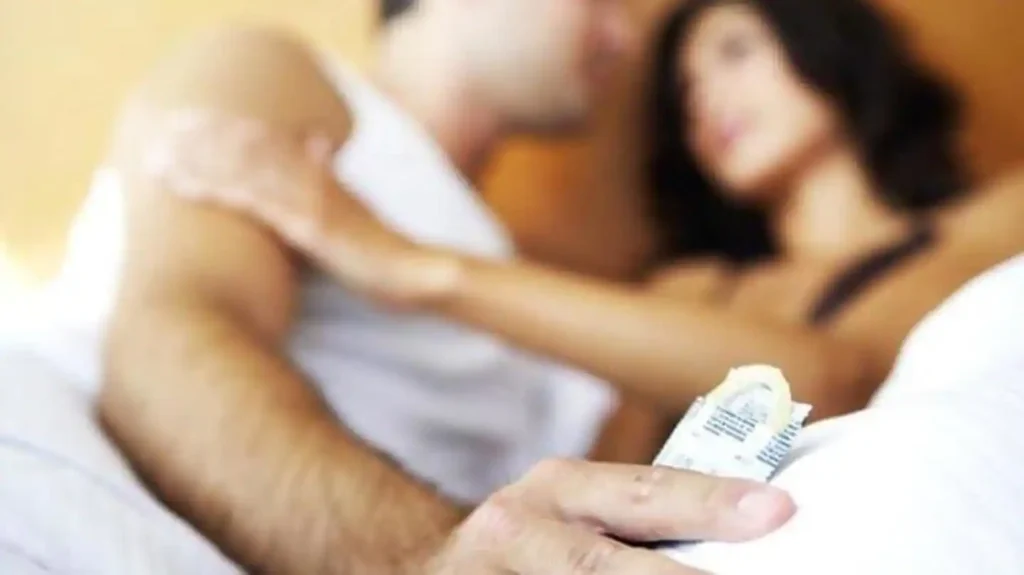

The male partner withdraws before ejaculation to prevent sperm from entering the vagina. This method requires great self-control and is less effective than other natural methods due to the possibility of pre-ejaculate containing sperm.
5. Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM)
Exclusively breastfeeding mothers may experience a temporary pause in ovulation. This method is effective for up to six months postpartum as long as breastfeeding occurs frequently and no menstrual periods have resumed.
6. Symptom-Thermal Method
A combination of the basal body temperature, cervical mucus, and calendar methods increases accuracy in identifying the fertile window. Couples can use multiple signs to confirm when to abstain from intercourse.
7. Abstinence and Periodic Abstinence
Completely avoiding sexual intercourse or abstaining during fertile days is a natural and effective way to prevent pregnancy. This requires a high level of discipline and commitment.
How to Avoid Side Effects From Hormonal Birth Control
Hormonal birth control, such as pills, patches, injections, and implants, is highly effective in preventing pregnancy, but it can sometimes cause side effects like weight gain, mood swings, nausea, and headaches. While side effects vary from person to person, there are several ways to minimize or avoid them:
1. Choose the Right Type of Hormonal Birth Control
Not all hormonal contraceptives have the same formulation. Some contain only progestin, while others combine estrogen and progestin. If you experience side effects with one type, switching to another may help. For example, those sensitive to estrogen might do better with a progestin-only pill or hormonal IUD.
2. Give Your Body Time to Adjust
Many side effects occur during the first few months as your body adapts to hormonal changes. If symptoms are mild, consider waiting two to three months before switching methods, as they often subside with time.
Recommended: Creighton Method of Natural Family Planning
3. Take Birth Control at the Same Time Every Day
For pills, consistency is key to maintaining hormone levels and preventing side effects like nausea and spotting. Setting a daily reminder can help with adherence.
4. Manage Nausea by Taking Pills With Food
If you experience nausea, taking your pill with food or before bedtime may reduce discomfort. Avoiding spicy or greasy foods during the adjustment period can also help.
5. Stay Hydrated and Eat a Balanced Diet
Drinking enough water and eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and fiber can prevent bloating and weight gain associated with hormonal birth control. Reducing sodium intake may also help with water retention.
6. Exercise Regularly to Combat Weight Gain and Mood Swings
Engaging in regular physical activity can help prevent weight gain, improve mood, and reduce bloating. Activities like yoga and meditation may also help manage stress and hormonal fluctuations.
7. Consider Lower-Dose or Non-Hormonal Alternatives
If side effects persist, speak to your doctor about trying a lower-dose hormonal method. Some people may benefit from switching to a copper IUD, which is non-hormonal and free of hormonal side effects.
8. Monitor Mental Health and Mood Changes
Hormonal fluctuations can sometimes lead to mood swings, anxiety, or depression. If you notice significant changes in your emotions, discuss alternative contraceptive options with your healthcare provider.
Recommended: Family Planning Options for Couples Over 35
9. Address Acne or Skin Changes With Proper Skincare
Some birth control methods improve acne, while others may cause breakouts. Using a gentle skincare routine and avoiding oily products can help manage changes in skin condition.
10. Consult Your Doctor for Persistent or Severe Side Effects
If side effects are severe or last longer than a few months, it’s best to consult a healthcare provider. They can help adjust your prescription or recommend alternative methods that better suit your body’s needs.
Managing Birth Control Side Effects Naturally
Hormonal birth control methods, such as pills, patches, injections, and implants, can sometimes cause side effects like nausea, weight gain, mood swings, headaches, and bloating. While these effects often improve over time, there are natural ways to manage them and support your body’s balance.
1. Eat a Nutrient-Rich Diet

A healthy diet can help counteract side effects like bloating, water retention, and weight gain. Increase your intake of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while reducing processed foods and excess salt. Foods rich in magnesium and potassium, like bananas and leafy greens, can help prevent bloating.
2. Stay Hydrated
Drinking plenty of water helps flush out excess hormones, reduce water retention, and improve digestion. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water daily to prevent bloating and headaches.
Recommended: 6 Family Planning Tips for Women with PCOS
3. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity can help regulate weight, improve mood, and boost energy levels. Low-impact exercises like walking, yoga, or swimming can also relieve bloating and improve circulation.
4. Use Herbal Remedies
Some herbs may help balance hormones naturally. Ginger or peppermint tea can ease nausea, while chamomile and lavender can reduce anxiety and improve sleep. However, consult your doctor before taking any herbal supplements, as some may interfere with birth control effectiveness.
5. Get Enough Sleep
Hormonal fluctuations can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to fatigue and mood swings. Maintain a regular sleep schedule and practice good sleep hygiene by avoiding screens before bed and creating a relaxing bedtime routine.
6. Manage Stress with Relaxation Techniques
Stress can worsen hormonal side effects like mood swings and headaches. Meditation, deep breathing, and mindfulness techniques can help manage stress and promote emotional balance.
7. Reduce Caffeine and Alcohol Intake
Excess caffeine can contribute to anxiety and breast tenderness, while alcohol may intensify mood swings. Cutting back on these can help minimize birth control-related side effects.
8. Take a Probiotic for Gut Health
Hormonal birth control can sometimes affect gut bacteria, leading to bloating and digestive issues. Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables can support gut health and digestion.
Recommended: How To Prepare Financially And Emotionally For Family Planning
9. Track Your Symptoms
Keeping a journal of your symptoms can help identify patterns and triggers, making it easier to adjust your lifestyle and dietary choices accordingly.
10. Consult a Healthcare Provider
If natural remedies don’t relieve your symptoms, speak with a doctor. They can suggest alternative birth control methods or make adjustments to better suit your body.
Conclusion
Choosing and managing birth control is a personal journey that requires careful consideration of health, lifestyle, and individual preferences. While hormonal birth control is highly effective, it may come with side effects that can often be managed through natural lifestyle adjustments, proper nutrition, and stress management. Exploring different options, such as non-hormonal methods, may also help those who are sensitive to hormonal changes.
