Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a common issue that affects many men, especially as they get older. One possible cause of ED is low testosterone, the hormone that plays a big role in a man’s sex drive and overall health. Because of this, some men consider testosterone therapy to help with their symptoms.
Recommended: Can Hydrogen Peroxide be Used For Erectile Dysfunction?
But does testosterone therapy actually work for treating ED?
In this article, we’ll look at how testosterone affects erections, when therapy might help, and what to know before starting treatment.
What Is Erectile Dysfunction?
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the ongoing difficulty in getting or keeping an erection firm enough for sexual activity. While it’s normal for men to occasionally experience this issue, frequent or persistent problems may point to an underlying condition that needs attention. ED becomes more common with age, but it can affect men at any stage of life.

The causes of erectile dysfunction can be physical, emotional, or a combination of both. Physical factors may include problems with blood flow, nerve function, or hormone levels, such as low testosterone. Psychological factors like stress, anxiety, or depression can also play a role. In many cases, ED is linked to other health issues such as diabetes, heart disease, or side effects from certain medications.
Understanding Testosterone and Its Role in Male Sexual Health
Testosterone is the main male sex hormone, and it plays a key role in many aspects of a man’s health. It affects muscle mass, bone density, red blood cell production, mood, and most importantly for this topic, sexual function.
Recommended: Do Raw Eggs Increase Testosterone?
One of testosterone’s major roles is regulating libido, or sex drive. When testosterone levels are within a healthy range, most men experience a normal interest in sexual activity. It also supports the function of the tissues and nerves involved in achieving an erection. However, it’s important to understand that testosterone alone doesn’t directly cause an erection—it works alongside other systems in the body, including blood flow and nerve signals.
When testosterone levels drop too low—a condition known as low testosterone or hypogonadism—some men may notice reduced sexual desire, fatigue, mood changes, and sometimes difficulty with erections. But low testosterone is not always the sole cause of erectile dysfunction. Many men with ED have normal testosterone levels, and their symptoms may be due to other health issues.
How Testosterone Therapy Works
Testosterone therapy helps men with low testosterone (Low T) by restoring hormone levels to a healthy range. This can improve symptoms like low libido, fatigue, and, in some cases, erectile dysfunction—especially when ED is caused by hormonal imbalance.
There are several delivery methods, including injections, gels, patches, pellets, and tablets, each with pros and cons. While TRT can enhance sexual desire and overall vitality, its effect on erections is often indirect. It’s more effective when low testosterone is a contributing factor to ED and may work best when combined with other treatments like PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., Viagra).
Recommended: Do Raw Eggs Increase Testosterone?
Results aren’t immediate—improvements in libido may appear within weeks, but noticeable changes in erectile function can take several months. Regular medical monitoring is essential to adjust dosage and minimize side effects.
How Effective Is Testosterone Therapy for ED?
Testosterone therapy can be moderately effective for erectile dysfunction—but only if low testosterone is a contributing factor. It works best in men who have confirmed Low testosterone along with symptoms like low libido and fatigue.
TRT may improve sexual desire and support better erections over time, especially when combined with ED medications like Viagra. However, it’s less effective if testosterone levels are normal or if ED is caused by other factors like poor circulation or psychological issues.
Results take time—libido may improve in a few weeks, but erectile function can take 3 to 6 months to show noticeable changes.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Testosterone Therapy
Testosterone therapy (TRT) can offer significant benefits for men with low testosterone, but it also carries potential risks and side effects that need to be understood. Below are the common side effects:
1. Acne and Oily Skin
Testosterone increases oil production in the skin, which can lead to clogged pores and acne. This happens because the hormone stimulates sebaceous glands to produce more oil. As a result, some men may experience breakouts, particularly on the face, chest, or back. Acne can usually be managed with topical treatments, but severe cases may require medical attention.
Recommended: Why Is My Penis Head Losing Sensitivity?
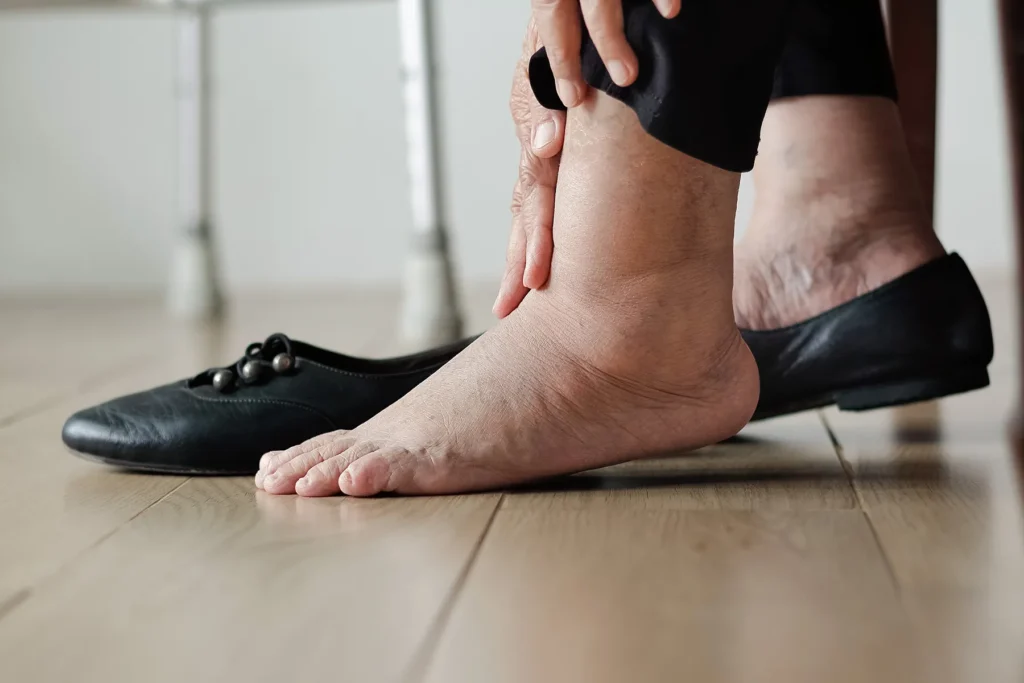
2. Fluid Retention or Swelling
Some men on TRT may notice swelling, particularly in the ankles, due to fluid retention. Testosterone causes the body to hold onto more sodium and water, leading to this unwanted side effect. While this may be mild in many cases, it can be uncomfortable or noticeable. Diuretics or other medications can help reduce the swelling, and regular monitoring of weight and fluid levels is important..
3. Breast Tenderness or Enlargement (Gynecomastia)
Some men may experience breast tenderness or even the development of enlarged breast tissue, a condition known as gynecomastia. Testosterone can be converted into estrogen in the body, which may lead to the growth of breast tissue. If this becomes an issue, medications like aromatase inhibitors may be used to block estrogen production, or in more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the excess tissue.
4. Mood Swings or Irritability
Testosterone therapy can affect mood and emotions. Some men experience irritability, mood swings, or even increased aggression. These changes occur because fluctuations in testosterone levels can impact the brain’s regulation of mood. While some men may feel an improvement in mood or overall well-being, others may struggle with heightened irritability or emotional changes. If mood swings are significant, adjusting the testosterone dose or changing the form of therapy might be necessary.
Recommended: How to Fix Delayed Ejaculation from Antidepressants
5. Sleep Apnea Worsening
For men who already suffer from sleep apnea, testosterone therapy can sometimes worsen the condition. Sleep apnea is a disorder where breathing stops and starts during sleep, and TRT may cause muscles in the throat to relax more, potentially increasing the risk of airway obstruction. This can result in more frequent pauses in breathing during sleep. Monitoring for sleep disturbances is important, and the use of a CPAP (Continuous Positive Airway Pressure) machine may be recommended to ensure proper breathing during sleep.
6. Cardiovascular Risks
Some studies have suggested that testosterone therapy may increase the risk of heart-related issues, such as heart attacks, strokes, or blood clots. The theory is that increasing red blood cell count and thickening the blood can raise blood pressure or cause clotting problems. However, the evidence is mixed, and some research suggests no increased risk when therapy is properly managed. Men with pre-existing heart conditions or cardiovascular risk factors should undergo careful monitoring while on TRT.
7. Prostate Health Concerns
Testosterone therapy can cause an increase in prostate-specific antigen (PSA) levels, a marker used to monitor prostate health. Although TRT does not cause prostate cancer, it may stimulate the growth of existing prostate tissue, potentially making prostate cancer (if present) grow faster. For this reason, regular monitoring of PSA levels is important. If PSA levels rise significantly, further testing, such as a prostate biopsy, may be necessary to rule out any underlying issues.
8. Fertility Issues
Testosterone therapy can reduce sperm production, leading to lower fertility in men. This happens because external testosterone supplementation can suppress the body’s natural testosterone production, which in turn affects the testes’ ability to produce sperm. While fertility issues may be reversible once TRT is stopped, it can take several months for sperm production to normalize. Men who are concerned about fertility should discuss this with their doctor and may choose to bank sperm before beginning treatment.
Recommended: Natural Ways to Increase Testosterone for Better Male Vitality
Alternative and Complementary Treatments for Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
In addition to testosterone therapy and standard ED medications, there are several alternative and complementary treatments that may help improve erectile function. These treatments can target physical, psychological, and lifestyle-related causes of ED. Below are the most commonly used alternatives:
PDE5 Inhibitors (Oral ED Medications)

Though not technically alternative, medications like sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis), and vardenafil (Levitra) remain among the most effective treatments for ED. They work by enhancing blood flow to the penis and are particularly helpful for men whose ED is related to vascular or age-related factors. These drugs can also be combined with other therapies for enhanced effectiveness.
Lifestyle Changes
Improving overall health can have a profound effect on erectile function. Regular physical activity enhances circulation, reduces stress, and helps maintain hormonal balance. Eating a heart-healthy diet—such as the Mediterranean diet—supports vascular health and testosterone production. Losing excess weight can reduce the risk of diabetes and heart disease, both of which are closely linked to ED. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake also significantly improve sexual health, as both substances negatively impact circulation and hormone levels.
Psychological Counseling and Sex Therapy
Many cases of ED are influenced or caused by psychological factors such as anxiety, depression, or relationship stress. Therapy, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and sex therapy, can be very effective in these cases. CBT helps men challenge and reframe negative thoughts that interfere with sexual performance, while sex therapy provides tools for communication and intimacy in relationships.
Recommended: Best Herbs For Male Fertility
Pelvic Floor Physical Therapy
Pelvic floor exercises, commonly known as Kegels, strengthen the muscles that support erectile function. These exercises target the pubococcygeus muscle, which plays a direct role in erection quality and ejaculation control. Studies have shown that regular pelvic floor training can restore or improve erectile function, especially in men with mild to moderate ED or those recovering from prostate surgery.
Vacuum Erection Devices (VEDs)
A vacuum erection device is a non-invasive mechanical tool that draws blood into the penis using suction. Once the erection is achieved, a constriction ring is placed at the base of the penis to maintain it. VEDs can be particularly helpful for men who cannot take oral ED medications or who have nerve damage.
Herbal and Natural Supplements
Some men turn to natural remedies in search of ED relief. Supplements such as L-arginine, Panax ginseng, yohimbine, and horny goat weed have been marketed for their potential to enhance blood flow and sexual function. While some small studies suggest modest benefits, the overall scientific support is limited, and the quality of supplements varies widely.
Conclusion
Testosterone therapy can help with erectile dysfunction, but only if low testosterone is part of the problem. It may improve sex drive and energy, and in some cases, help with erections. However, it’s not a guaranteed fix and won’t work for everyone.
The best way to know if it’s right for you is to get your hormone levels checked and talk to your doctor. Often, the most effective results come from a mix of treatments, including lifestyle changes, medication, and therapy—depending on what’s causing the ED.