Contraceptive implants are a popular long-term birth control option for many individuals looking for a reliable and convenient way to prevent pregnancy. These small, flexible rods are inserted under the skin and release hormones to stop ovulation, making them highly effective in preventing conception. However, a common concern among users is whether these implants can lead to infertility or make it harder to conceive after removal.
Recommended: Can Birth Control Cause Extreme Fatigue?
While hormonal birth control methods, including implants, can temporarily affect the menstrual cycle, many wonder if these changes have lasting effects on fertility.
In this blog, we’ll explore how contraceptive implants work, whether they impact fertility in the long run, and what to expect when trying to conceive after discontinuing their use.
What Are Contraceptive Implants?
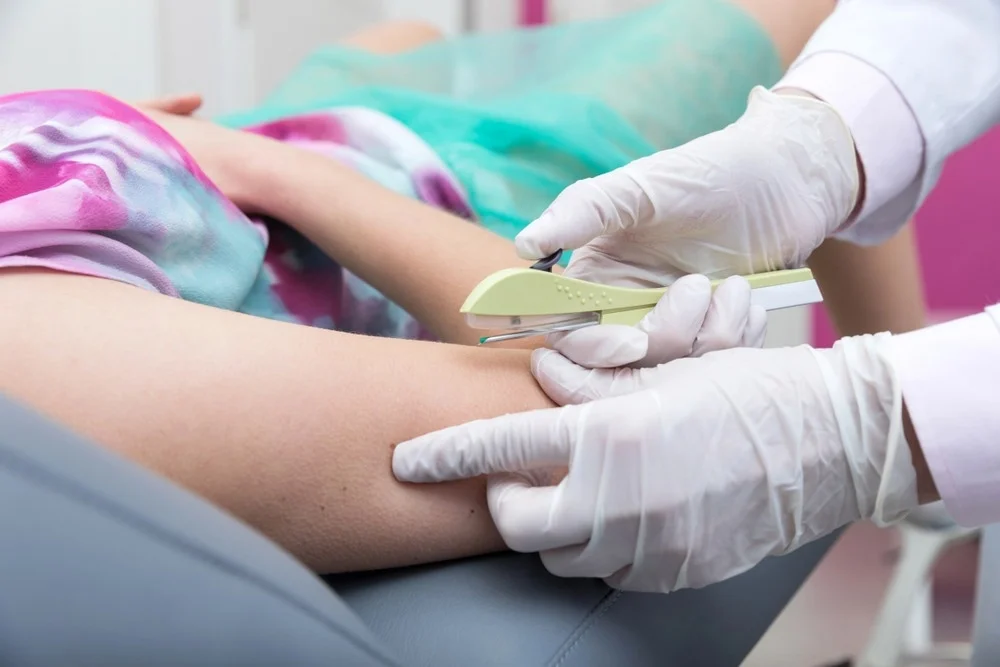
Contraceptive implants are small, flexible rods placed just beneath the skin of the upper arm to offer long-term birth control. They gradually release a hormone called progestin, which helps prevent pregnancy for three to five years, depending on the type of implant. Popular options like Nexplanon and Implanon are widely used due to their effectiveness and convenience.
How Do Contraceptive Implants Prevent Pregnancy?
These implants work by continuously releasing progestin, which prevents pregnancy through three key mechanisms:
- Suppressing Ovulation – Progestin prevents the ovaries from releasing eggs, eliminating the possibility of fertilization.
- Thickening Cervical Mucus – The hormone increases the thickness of cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to reach an egg.
- Altering the Uterine Lining – Progestin changes the uterine lining, making it less suitable for a fertilized egg to implant.
Recommended: Best Multivitamins For Going Off Birth Control
Due to these combined effects, contraceptive implants are among the most reliable birth control methods, with a success rate exceeding 99%. After removal, fertility typically returns quickly, and most individuals can conceive within a few months if they choose to.
Do Contraceptive Implants Cause Infertility?
Contraceptive implants do not cause permanent infertility. These small, hormone-releasing devices are designed to offer temporary birth control by steadily releasing progestin, which prevents pregnancy while the implant remains in place. Once removed, the body gradually resumes its natural reproductive cycle, and fertility is generally restored within a few months.
Most individuals regain their ability to conceive soon after removal, with many achieving pregnancy within a year. However, the time it takes for fertility to return can vary based on individual factors such as age, overall health, and any pre-existing reproductive conditions. If conception is delayed, it is more likely due to underlying fertility issues rather than the previous use of a contraceptive implant.
Overall, contraceptive implants are a highly effective and reversible birth control method. They do not have lasting effects on fertility, making them a reliable option for those seeking temporary contraception without long-term reproductive consequences.
Recommended: Can I Take Birth Control After Wisdom Teeth Removal?
How Long Does It Take to Regain Fertility After Implant Removal?
Fertility typically returns quickly after removing a contraceptive implant. Most individuals begin ovulating within a few weeks to a few months, with many able to conceive within a year. Some may even become pregnant as early as the first menstrual cycle after removal.
However, the exact timeframe for fertility restoration varies from person to person. Factors such as age, overall health, menstrual cycle regularity, and any pre-existing reproductive conditions can influence how soon ovulation resumes. While the implant itself does not cause infertility, those with underlying fertility issues may experience delays in conception unrelated to birth control use.
If pregnancy does not occur within a year of trying after implant removal, it may be beneficial to consult a healthcare provider to assess other potential factors affecting fertility.
Recommended: Creighton Method of Natural Family Planning
Possible Side Effects of Contraceptive Implants on Reproductive Health
Contraceptive implants are a reliable and reversible birth control method, but like any hormonal contraceptive, they can cause side effects that may impact reproductive health. These effects vary depending on individual hormonal responses and usually improve over time.
- Irregular Menstrual Cycles – Many individuals experience changes in their periods, such as irregular spotting, prolonged bleeding, or, in some cases, the absence of periods (amenorrhea). While this is not harmful, it can be concerning for some users.
- Hormonal Imbalance – The release of progestin can lead to symptoms such as mood swings, mild depression, headaches, acne, or breast tenderness. These symptoms often subside as the body adjusts to the implant.

- Delayed Return to Regular Ovulation – Although fertility typically returns quickly after implant removal, some individuals may take a few months for their menstrual cycle to normalize, especially if they previously had irregular periods.
- Ovarian Cysts – A small percentage of users may develop ovarian cysts, which are usually harmless and disappear on their own. However, in rare cases, they may cause discomfort or require medical attention.
- Changes in Libido – Some individuals may notice an increase or decrease in sexual desire due to hormonal shifts. This effect varies and may be influenced by other factors such as stress or overall health.
Recommended: 6 Family Planning Tips for Women with PCOS
While most side effects are temporary and manageable, those experiencing severe or prolonged symptoms should consult a healthcare provider for further evaluation and possible alternative contraceptive options.
Factors That May Affect Fertility After Implant Removal
Contraceptive implants do not cause infertility, but various factors can influence how quickly fertility returns after removal. While many individuals regain their ability to conceive within a few months, others may experience delays due to underlying health and lifestyle factors. Understanding these influences can help set realistic expectations and guide individuals in optimizing their reproductive health.
1. Age
Age plays a significant role in fertility. Women in their early 20s generally have the highest fertility rates, but as they approach their mid-30s and beyond, fertility naturally declines. This is due to a decrease in both the quantity and quality of eggs. Therefore, individuals who have used contraceptive implants for several years and are now in their late 30s or early 40s may find it harder to conceive, regardless of implant use.
Recommended: Family Planning Options for Couples Over 35
2. Hormonal Adjustment
After implant removal, the body needs time to regulate its natural hormone production. The implant works by releasing progestin, which prevents ovulation. Once removed, some individuals may experience a delay in ovulation as their body readjusts. For most people, ovulation resumes within a few weeks to a few months, but in some cases, it may take longer. If ovulation does not return within six months, it is advisable to seek medical advice.
3. Pre-Existing Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions can affect fertility and may cause delays in conception after implant removal:
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS): A common hormonal disorder that can cause irregular ovulation or anovulation (absence of ovulation).
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can disrupt menstrual cycles and ovulation.
- Endometriosis: A condition where tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, potentially affecting fertility.
- Diabetes and Other Metabolic Disorders: Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect ovulation and implantation.
4. Menstrual Cycle Regularity
Individuals with irregular periods before using the implant may take longer to conceive after removal. The implant itself can sometimes cause irregular menstrual cycles, and it may take a few months for the cycle to stabilize after discontinuation. Those who had regular cycles before implant use are more likely to resume normal ovulation quickly.
5. Lifestyle and Health Factors
Certain lifestyle habits can impact fertility, including:
- Diet and Nutrition: A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supports reproductive health. Nutrient deficiencies, such as low iron, folic acid, or vitamin D, can affect ovulation.
- Weight: Being overweight or underweight can disrupt hormone levels and ovulation. Maintaining a healthy BMI can improve fertility.
- Stress: High stress levels can interfere with hormone regulation and delay ovulation. Stress management techniques such as exercise, meditation, and counseling can help.
- Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking reduces egg quality and affects overall reproductive health, while excessive alcohol intake can disrupt hormonal balance and ovulation.
6. Partner’s Fertility
Fertility is not solely dependent on the individual who had the implant. The reproductive health of their partner is equally important. Factors such as sperm count, motility, and overall sperm quality play a crucial role in conception. If a couple has been trying to conceive for a year without success (or six months if the woman is over 35), it is recommended that both partners undergo fertility evaluations.

Recommended: How long does it take to conceive after stopping birth control?
When to Seek Medical Advice
While fertility typically returns within a few months after contraceptive implant removal, some individuals may experience delays. If conception does not occur within a reasonable timeframe, seeking medical advice can help identify potential underlying issues and provide guidance on the next steps. Here are some situations where consulting a healthcare provider is recommended:
1. Absence of Menstrual Periods
If menstruation does not return within three to six months after implant removal, it may indicate an underlying hormonal imbalance or ovulation issues. While some people experience temporary delays as their body readjusts, prolonged absence of periods should be evaluated by a doctor.
2. Irregular or Abnormal Menstrual Cycles
If periods return but are highly irregular, excessively heavy, or unusually light, this may suggest an underlying reproductive health issue such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, or endometriosis. A medical evaluation can help determine the cause and appropriate treatment.\
Recommended: Does Family Planning Affect Future Pregnancy?
3. Difficulty Conceiving After One Year
For individuals under 35 years old, it is generally advised to try conceiving for one year before seeking fertility assistance. However, if conception does not occur within this timeframe, a fertility evaluation is recommended.
For individuals over 35, it is best to seek medical advice after six months of trying to conceive, as fertility naturally declines with age.
4. Signs of Ovulation Problems

If there are signs that ovulation is not occurring regularly—such as missed periods, absent mid-cycle cervical mucus, or consistently negative ovulation test results—a doctor can assess hormone levels and recommend potential treatments to stimulate ovulation.
Recommended: How Soon After Tubal Reversal Can I Try To Conceive?
5. Pre-Existing Health Conditions
Individuals with a history of reproductive health issues such as PCOS, endometriosis, thyroid disorders, or diabetes should seek medical advice if they experience significant delays in conception. These conditions can affect ovulation and overall fertility, and a doctor can suggest personalized treatments or lifestyle modifications.
6. Partner’s Fertility Concerns
Fertility issues are not solely dependent on the person who had the contraceptive implant. If a couple has been trying to conceive for a long time without success, it may be necessary for the partner to undergo a semen analysis to assess sperm count, motility, and overall reproductive health.
Recommended: Can a Woman Have an Orgasm After Menopause?
7. Other Symptoms Indicating Reproductive Health Issues
Seek medical advice if experiencing symptoms such as:
- Chronic pelvic pain
- Painful periods or intercourse
- Unexplained weight gain or loss
- Signs of hormone imbalance (e.g., acne, excessive hair growth, mood swings)
Conclusion
Contraceptive implants are a highly effective and reversible method of birth control, offering long-term protection without significant long-term impacts on fertility. While fertility typically returns within a few months after implant removal, several factors such as age, underlying health conditions, and individual reproductive health may influence the timeline. It is essential to remember that fertility is a complex process, and the return of normal ovulation may vary from person to person.
If pregnancy does not occur within a reasonable timeframe, or if there are any concerns about menstrual irregularities, ovulation problems, or other reproductive health issues, seeking medical advice is crucial. Healthcare professionals can provide tailored guidance, identify potential health concerns, and recommend appropriate treatments or lifestyle adjustments to enhance fertility.
Ultimately, contraceptive implants do not cause infertility, and the vast majority of individuals can successfully conceive after their removal. Patience, proper healthcare, and tracking fertility signs can help optimize the chances of conception, making it possible for most individuals to achieve their reproductive goals.
