Nexplanon is a popular birth control option chosen for its convenience and long-lasting protection. A single implant can prevent pregnancy for up to three years and is inserted just under the skin of the upper arm. While many women use Nexplanon without any issues, it’s important to understand that in rare cases, the body may react negatively to the implant. This can range from mild side effects to more serious signs that your body may be rejecting it. Knowing the difference between what’s normal and what’s not is essential for staying safe and healthy.
In this post, we’ll cover the signs of implant rejection, when to seek medical help, and what options are available if problems arise.
Nexplanon and How It Works
Nexplanon is a form of long-acting reversible contraception that is widely used for its convenience and high effectiveness. It is a small, flexible plastic rod, about the size of a matchstick, which is inserted just under the skin of your upper arm by a trained healthcare provider. The insertion process is quick and usually done in a doctor’s office using local anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
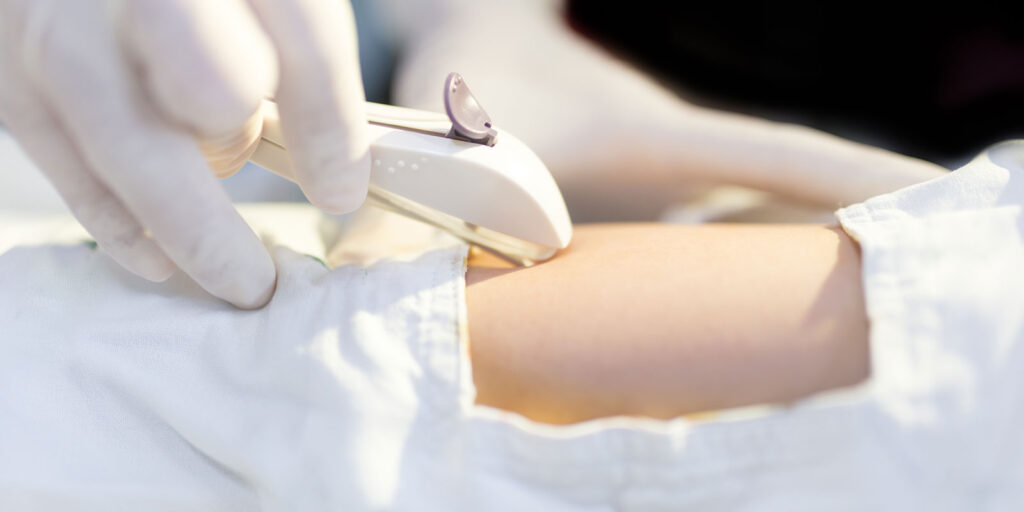

Once inserted, Nexplanon releases a steady, low dose of a hormone called etonogestrel, which is a synthetic form of progestin. This hormone works in several ways to prevent pregnancy. First, it stops ovulation, meaning your ovaries do not release eggs. Second, it thickens the mucus in the cervix, making it difficult for sperm to enter the uterus. Third, it thins the lining of the uterus, which can help prevent a fertilized egg from implanting.
Recommended: Can the Copper IUD Cause Bad Body Odour or a Metallic Smell?
Nexplanon is more than 99 percent effective at preventing pregnancy and offers protection for up to three years. It is a good option for people who want long-term birth control without the need for daily pills or regular doctor visits. However, as with any medical device, it is important to be aware of how your body reacts after insertion and to watch for any signs of complications or unusual side effects.
What Does It Mean When Your Body Rejects an Implant?
When your body “rejects” a contraceptive implant like Nexplanon, it means that your system is responding negatively to the device in a way that goes beyond normal side effects. Rejection can involve your body physically pushing the implant out, reacting with an ongoing immune or inflammatory response, or developing complications at the insertion site. While true rejection is rare, it is important to recognize the difference between expected side effects and signs that something more serious might be happening.
In some cases, rejection may present as persistent pain, swelling, or redness around the insertion site. The implant might shift, become more visible under the skin, or even begin to protrude. In very rare situations, the body can try to expel the implant completely. These symptoms could indicate that your body is not tolerating the foreign object, possibly due to improper placement, an infection, or an allergic reaction to materials in the implant.
Recommended: How Reliable Are Natural Methods vs Hormonal Ones for Pregnancy Prevention?
Early Signs Your Body May Be Rejecting Nexplanon
While most people tolerate Nexplanon well, early signs of implant rejection or complications can appear within days or weeks after insertion. If you notice any of the following symptoms, it’s important to speak with your healthcare provider:
- Persistent or increasing pain at the implant site
- Redness, warmth, or swelling that doesn’t improve over time
- Skin irritation or rash near the implant
- The implant becomes more visible or begins to protrude from the skin
- The implant feels like it’s moving or shifting significantly under the skin
- Tingling, numbness, or weakness in the arm or hand on the side where the implant was inserted
- Unusual or prolonged bleeding that is heavier or more frequent than expected
- Fever or chills, which may indicate an infection
- Pus or fluid discharge from the insertion site
- Hard lump or buildup of scar tissue forming around the implant

Other possible side effects that aren’t as common include:
- Headaches
- Breast pain
- Nausea
- Weight gain
- Ovarian cysts
- Pain or bruising on your arm where the implant was inserted
- An infection where the implant was inserted
Recommended: What Early Symptoms Might Signal a Failed IUD?
If you don’t like the way the implant makes you feel after you’ve had it for a few months, talk with a nurse or doctor, like the ones at your local Planned Parenthood health center. They may suggest a different birth control method.
Infection vs. Rejection: How to Tell the Difference
It’s important to understand the difference between an infection and implant rejection, as the symptoms can sometimes overlap. Both may cause discomfort, redness, or swelling near the insertion site, but they have different causes and require different treatments. An infection happens when bacteria enter the body through the skin, usually during or after the insertion process. Rejection, on the other hand, is your body’s immune system reacting to the presence of the implant itself.
Signs of infection often include increasing redness, warmth, tenderness, and swelling around the implant site. You may also notice pus, an unpleasant smell, or fluid draining from the area. In some cases, you might develop a fever, feel fatigued, or experience chills. These symptoms usually appear soon after insertion and tend to worsen if left untreated. Infections require medical attention and are typically treated with antibiotics or, in some cases, removal of the implant.
Recommended: Should I Inform My Doctor if My IUD Was Dislodged Even if I’m Not Sexually Active?
Rejection symptoms, however, may develop more gradually and are often centered around your body not tolerating the implant. The implant may shift, push toward the surface of the skin, or become visible or painful. You might also feel ongoing irritation, itching, or sensitivity in the arm. Unlike infections, rejection doesn’t always involve systemic symptoms like fever. If you’re experiencing any concerning signs, it’s best to have a healthcare provider examine the site to determine the cause and recommend the right treatment.
Signs the Implant Has Shifted or Migrated
Although rare, one potential complication with the Nexplanon implant is that it can move from the site where it was originally inserted. Migration usually happens within a small area near the insertion site, but in very rare cases, it may travel further into the arm or even toward the bloodstream. Recognizing the signs of implant migration early is important for preventing complications.
1. You Can’t Feel the Implant Where It Was Placed
After insertion, your healthcare provider will usually show you how to feel the implant just under the skin. It should feel like a small, flexible rod. If you suddenly can’t locate it or feel it has moved, that could be a sign that it has shifted.
2. Pain or Discomfort in the Arm
If the implant has moved, it may press on nearby nerves or tissue. This can cause:
- Aching or sharp pain in the arm
- Discomfort that increases with movement
- Pain when touching or pressing the area
3. Numbness or Tingling in the Hand or Arm

Movement of the implant near a nerve can lead to:
- Tingling or a “pins and needles” sensation
- Numbness in the fingers, hand, or arm
- Weakness or reduced range of motion
Recommended: Is the Copper IUD Better for Heavy Periods?
4. Visible Movement or Change in Implant Location
Sometimes, you may actually see the implant protruding or notice it’s in a different spot than before. While it’s normal for the implant to be slightly mobile under the skin, any significant shift should be evaluated.
5. Implant Seems Deeper or Harder to Detect
If the implant has migrated deeper into the tissue, it might be difficult or impossible to feel. This can be a concern because it may complicate removal later on.
6. Unusual Bruising or Swelling
While minor bruising is common after insertion, if you experience new or worsening bruising, swelling, or redness weeks or months after the procedure, it could indicate a problem such as migration or local tissue reaction.
Conclusion
Nexplanon is a highly effective and convenient form of birth control for many people, but it’s important to stay aware of how your body is responding to it. While mild side effects are common and often temporary, certain symptoms—like pain, implant movement, unusual bleeding, or signs of infection—may signal a more serious issue, including implant rejection or migration.
Your health and comfort should always come first. If something doesn’t feel right, trust your instincts and reach out to your healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent complications and help you find a contraceptive method that’s safe and suitable for your body.