Breast surgery, whether it’s for cosmetic enhancement, reconstruction after mastectomy, or biopsy procedures, has become increasingly common in today’s society. With advancements in medical technology and techniques, more women are opting for surgical interventions to address various concerns related to their breasts. However, along with the benefits of these procedures come potential risks and complications, among which post-surgical infections are a significant concern.
Understanding the signs of infection after breast surgery is paramount for patients, caregivers, and medical professionals alike. Infections can not only prolong recovery time but also lead to serious health complications if left untreated. Therefore, this guide aims to provide a comprehensive guide to recognizing the signs of infection after breast surgery, empowering readers with the knowledge to identify potential issues and seek appropriate medical attention promptly.
While breast surgery can yield transformative results and positively impact a person’s confidence and quality of life, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential risks involved. By being aware of the signs of infection and understanding the importance of early detection and treatment, women undergoing breast surgery can take an active role in safeguarding their health and optimizing their surgical outcomes.
Recommended: How Soon After Tubal Reversal Can I Try To Conceive?
So, let’s delve deeper into this topic to equip ourselves with the necessary knowledge and awareness to navigate the post-operative period with confidence and peace of mind.
Understanding Breast Surgery
Breast surgery encompasses a range of procedures undertaken for various medical and cosmetic reasons. Understanding the different types of breast surgery, the reasons behind them, and the typical processes involved can help patients prepare for their journey and set realistic expectations for recovery and outcomes. Here, we delve into the common types of breast surgery and the general process each entails.
Types of Breast Surgery
- Breast Augmentation: Aimed at increasing breast size or improving shape, this procedure involves the insertion of implants (saline or silicone) or, in some cases, fat transfer to the breast.
- Breast Reduction: This surgery is performed to reduce the size of the breasts, often to alleviate physical discomfort such as neck and back pain or skin irritation under the breasts. It involves the removal of excess breast tissue and skin.
- Breast Reconstruction: Typically offered to women who have undergone a mastectomy due to breast cancer, reconstruction aims to restore the breast’s appearance. This can be achieved using implants, autologous tissue (tissue from elsewhere in the body), or a combination of both.
- Breast Lift (Mastopexy): Aimed at addressing sagging or drooping breasts, this procedure involves removing excess skin and tightening the surrounding tissue to reshape and support the new breast contour.
- Mastectomy: A surgical procedure to remove one or both breasts, partially (segmental mastectomy) or completely (total mastectomy), primarily used as a treatment for breast cancer.
- Lumpectomy: Also known as breast-conserving surgery, this involves the removal of the tumor and a small margin of surrounding tissue while preserving most of the breast. It’s often followed by radiation therapy.
The Surgical Process
- Preparation: Prior to any breast surgery, patients undergo a thorough evaluation which may include a medical history assessment, physical examination, and imaging tests. Patients are advised on how to prepare for surgery, including guidelines on eating, drinking, and medication adjustments.
- Anesthesia: Breast surgeries are performed under anesthesia to ensure the patient’s comfort. The type of anesthesia (general or local with sedation) depends on the specific procedure and patient preferences.
- The Procedure: Surgical techniques vary significantly depending on the type of surgery being performed. Incision patterns and locations, the use of implants or autologous tissue, and the extent of tissue alteration or removal are tailored to each patient’s needs and desired outcomes.
- Recovery: Post-operative care is crucial for a smooth recovery. Patients receive instructions on caring for their surgical sites, medications to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, and activity restrictions. Follow-up appointments are scheduled to monitor healing and address any concerns.
Recommended: Can You Drink Alcohol After Taking Abortion Pill?
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, breast surgeries carry risks. These may include infection, bleeding, scarring, changes in breast sensation, and dissatisfaction with cosmetic outcomes. Understanding these risks and knowing how to spot signs of complications, such as infection, is crucial for patients undergoing breast surgery.
Understanding the nuances of breast surgery can empower patients, helping them to make informed decisions and actively participate in their care and recovery process.
What Causes Infections After Breast Surgery?
Infections after breast surgery, as with any surgical procedure, occur when bacteria or other pathogens enter the wound site. Despite stringent sterilization techniques and preventive measures, the risk of infection cannot be entirely eliminated. Understanding how infections develop and the factors that increase this risk is crucial for prevention and early detection.
How Infections Develop
- Surgical Site Infections (SSIs): These are the most common infections following breast surgery. They occur at the site of the incision and can affect either the skin and tissue on top of the muscle (superficial) or deeper tissues within the breast. SSIs are typically caused by bacteria that are already present on the skin or those that enter the surgical site during or after the procedure.
- Internal Infections: Less commonly, an infection can develop inside the breast, within the tissue, or around implants (if used). These infections may result from bacteria introduced during surgery or, occasionally, from bacteria entering the bloodstream and migrating to the surgical area.
Factors Increasing the Risk of Infection
- Type and Length of Surgery: Longer surgeries and those involving implants (such as breast augmentations or reconstructions) have a higher risk of infection. The complexity of the procedure and the time the surgical site is exposed can contribute to this risk.
- Personal Health and Immune System Status: Women with weakened immune systems, whether due to chronic conditions (like diabetes), certain medications, smoking, or obesity, are at a higher risk of developing infections. A healthy immune system is critical for fighting off potential infections during the recovery process.
- Post-operative Care and Environment: How the surgical site is cared for after the procedure plays a significant role in preventing infection. Proper wound care, hygiene, and following the surgeon’s instructions are essential. Additionally, the environment in which a patient recovers, including the cleanliness of the surroundings and the presence of contaminants, can influence the risk of infection.
Recommended: Top 6 Signs Of Poor Egg Quality You Should Know
Understanding these causes and risk factors is the first step toward prevention. By addressing these aspects proactively, individuals undergoing breast surgery can significantly reduce their risk of developing post-surgical infections. This includes choosing a reputable surgical facility, ensuring good overall health before the procedure, and adhering to all post-operative care instructions.
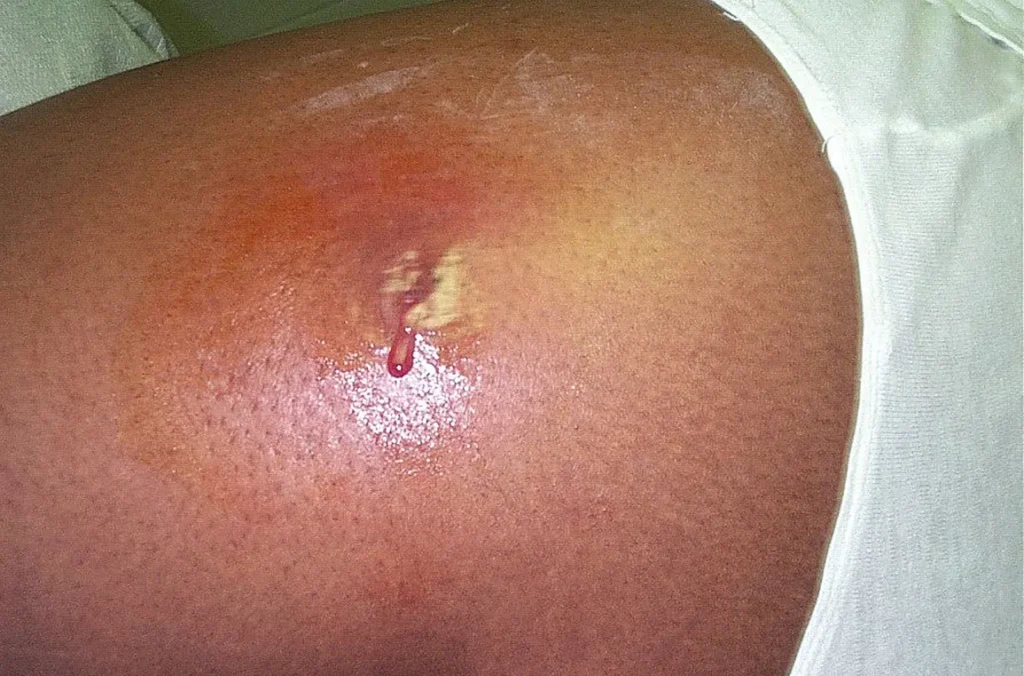
Early Signs of Infection After Breast Surgery
After undergoing breast surgery, it’s crucial to monitor the surgical site and overall health for signs of infection. Early detection and treatment of infections can prevent more serious complications. Here are key signs of infection that patients and caregivers should be aware of:
1. Redness and Swelling
It’s normal to experience some degree of redness and swelling at the surgical site after breast surgery. However, if the redness expands or becomes more intense, and the swelling increases or doesn’t gradually improve, it may indicate an infection.
Any significant increase in redness or swelling, especially if accompanied by warmth or heat over the area, should prompt a consultation with a healthcare provider.
2. Increased Pain or Tenderness
Some pain and discomfort are expected after breast surgery, but this should generally follow a predictable course of improvement. If pain intensifies rather than diminishes over time, or if new pain develops after an initial period of improvement, it could signal an infection. Increased tenderness to touch around the surgical site is also a concerning sign.
3. Fever and Chills
A fever (a temperature of 100.4°F or higher) following surgery can be a sign of infection. Chills or a feeling of being unusually cold can also accompany a fever as part of the body’s response to an infection.
4. Discharge from the Surgical Site
A clear or slightly yellowish fluid is common in the first few days after surgery. However, if the discharge becomes increasingly thick, yellow, green, or bloody, it may indicate an infection. An increase in the amount of discharge or a change in its consistency can also be a sign.
5. Unusual Odor from the Incision Site
While some odor can be normal, especially if a dressing has been in place for a while, a foul or unusual smell emanating from the incision site can be a sign of bacterial infection.
Recognizing these early signs of infection and seeking prompt medical evaluation can make a significant difference in the outcome. Treatment may involve antibiotics, wound care, or in some cases, additional surgery to address the infection.
Recommended: Can You Be a Surrogate With Your Tubes Removed?
It’s important for patients to follow their surgeon’s post-operative care instructions carefully and maintain open communication with their healthcare team throughout the recovery process. Being informed and vigilant can help ensure a smoother recovery and reduce the risk of complications after breast surgery.
Diagnosing and Treating Infections After Breast Surgery
When an infection is suspected following breast surgery, timely and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating the appropriate treatment. Here’s an overview of the process for diagnosing and treating infections after breast surgery:
Medical Evaluation and Diagnosis
- Physical examination: The first step in diagnosing an infection is a thorough physical examination by a healthcare provider. This includes inspecting the surgical site for signs of infection such as redness, swelling, warmth, and discharge. The provider will also check for fever and other systemic signs of infection.
- Laboratory tests and imaging: In some cases, further diagnostic tests may be necessary to identify the infection and its severity. This can include blood tests to look for markers of infection (such as a high white blood cell count) and cultures of any discharge to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection. Imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI may be used to assess the extent of the infection, especially if there is concern about an abscess or infection around an implant.
Treatment Options
- Antibiotics: Most infections can be treated effectively with antibiotics. The choice of antibiotic may initially be broad-spectrum, covering a wide range of bacteria. It might be adjusted based on the results of culture tests to target the specific bacteria causing the infection. Antibiotics may be given orally or intravenously, depending on the severity of the infection.
- Drainage of abscesses: If an abscess (a collection of pus) forms, it may need to be drained. This can sometimes be done with a needle and syringe in a minimally invasive procedure guided by ultrasound. In more severe cases, surgical drainage may be required.
- Possible revision surgery in severe cases: In cases where the infection is severe, involves an implant, or doesn’t respond to other treatments, additional surgery may be necessary. This could involve removing infected tissue or, in some cases, removing an implant until the infection is resolved.
Importance of Following Post-Surgical Care Instructions
- Maintaining cleanliness of the surgical site: Keeping the incision area clean and dry as per the surgeon’s instructions is vital for preventing infection. Patients will be advised on how to care for their surgical site, including instructions on bathing and changing dressings.
- Adhering to prescribed medication schedules: It’s crucial to take all medications, especially antibiotics, exactly as prescribed to effectively treat infection and prevent antibiotic resistance.
- Regular follow-up appointments: Attending all scheduled follow-up appointments allows the healthcare provider to monitor the recovery process and catch any signs of infection early.
Recommended: Hair Fall After Pregnancy Home Remedy
Early and effective treatment of infections following breast surgery is key to ensuring a smooth recovery and minimizing the risk of complications. Patients should be encouraged to promptly report any signs of infection to their healthcare provider and to follow all post-operative care instructions closely. With proper care and vigilance, most infections can be effectively managed, allowing for a safe and successful recovery.

Preventative Measures to Reduce the Risk of Infection
Reducing the risk of infection following breast surgery begins well before the procedure and continues through the post-operative period. Here are essential strategies for patients and healthcare providers to minimize the risk of infection:
1. Pre-surgical Care
Patients may be advised to use a special antibacterial soap or solution to cleanse the surgical area before the procedure. This can help reduce the presence of bacteria on the skin that could potentially cause an infection.
Patients should aim to be in the best possible health prior to surgery. This includes managing chronic conditions like diabetes, quitting smoking, and maintaining a healthy weight. A strong immune system is better equipped to fend off potential infections.
2. Post-surgical Practices
Following the surgeon’s instructions for caring for the incision is crucial. This typically includes keeping the area clean and dry, properly changing dressings, and avoiding submerging the surgical site in water (e.g., baths, swimming pools) until advised it’s safe to do so.
Patients should be educated on the signs of infection to watch for and instructed to report any concerns immediately. Prompt attention to symptoms like increased pain, redness, or fever can lead to early intervention and treatment.
Adhering to activity restrictions and recommendations from the healthcare provider is essential to prevent strain on the surgical site, which can promote healing and reduce the risk of infection. This includes avoiding heavy lifting and vigorous exercise for a specified period.
3. Lifestyle Modifications
Good nutrition plays a significant role in healing and immune function. Patients should focus on a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins to support tissue repair and fight off infections. Adequate hydration is also important for overall health and recovery.
Beyond the immediate post-operative period, patients should continue to take precautions to avoid infection. This includes avoiding direct sun exposure on the surgical scars, which can weaken the skin, and continuing to practice good hygiene.
4. Environmental Considerations
Ensuring that the recovery environment is clean and free of potential contaminants can help reduce the risk of infection. This includes regular cleaning of surfaces, changing bed linens and towels frequently, and avoiding contact with pets that might carry bacteria.
5. Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics before or immediately after surgery as a preventive measure against infection. It’s important for patients to follow these prescriptions as directed.
Patients should feel empowered to ask questions and raise concerns with their healthcare team at any point before or after surgery. Open communication can ensure that any potential issues are addressed promptly.
Recommended: Why Do Tampons Leak When Not Full?
By taking comprehensive preventative measures, patients and healthcare providers can work together to significantly reduce the risk of infection after breast surgery. While not all infections can be prevented, adherence to these strategies can lead to a safer recovery and more successful surgical outcomes.
FAQs
How soon after breast surgery can an infection occur?
Infections can occur at any time after surgery, but they most commonly develop within the first few weeks post-operation. It’s important to monitor the surgical site closely during the initial healing period.
Should I be concerned about a low-grade fever after my breast surgery?
A low-grade fever is not uncommon in the first 24 hours after surgery. However, a fever that develops or persists beyond the initial post-operative period, especially if accompanied by other signs of infection, should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Can an infection after breast surgery be treated at home?
Home remedies should not replace medical treatment for infections after surgery. While certain measures can support healing (such as rest and proper wound care), antibiotics or other medical interventions are often necessary to treat an infection effectively.
Can an infection affect the outcome of my breast surgery?
If detected and treated early, most infections will not have a long-term impact on the surgical outcome. However, severe or untreated infections can lead to more significant complications, including impacts on the aesthetic outcome or the need for additional surgery.
Is it normal to have some discharge from the surgical site after breast surgery?
Yes, some discharge, particularly clear or slightly yellow fluid, is normal in the first few days after surgery. However, if the discharge increases, changes color, or develops a foul odor, it may indicate an infection and should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
While the prospect of infection following breast surgery can be concerning, understanding the signs, knowing how to respond, and taking proactive measures to prevent infection can greatly reduce risks. By being informed and vigilant, patients can navigate their post-operative journey with confidence.
It’s crucial to maintain open communication with healthcare providers and adhere strictly to their guidance. Remember, early detection and treatment are key to a swift recovery. Armed with the right knowledge and precautions, patients can focus on healing and enjoying the positive outcomes of their breast surgery.
